Hydrogen Sulfide, H2S
Jim Shorey
H2S gas is commonly measured by instruments using both UV fluorescence and a Heated Converter.
Hydrogen Sulfide, H2S gas emissions are often a result from oil & gas production facilities.
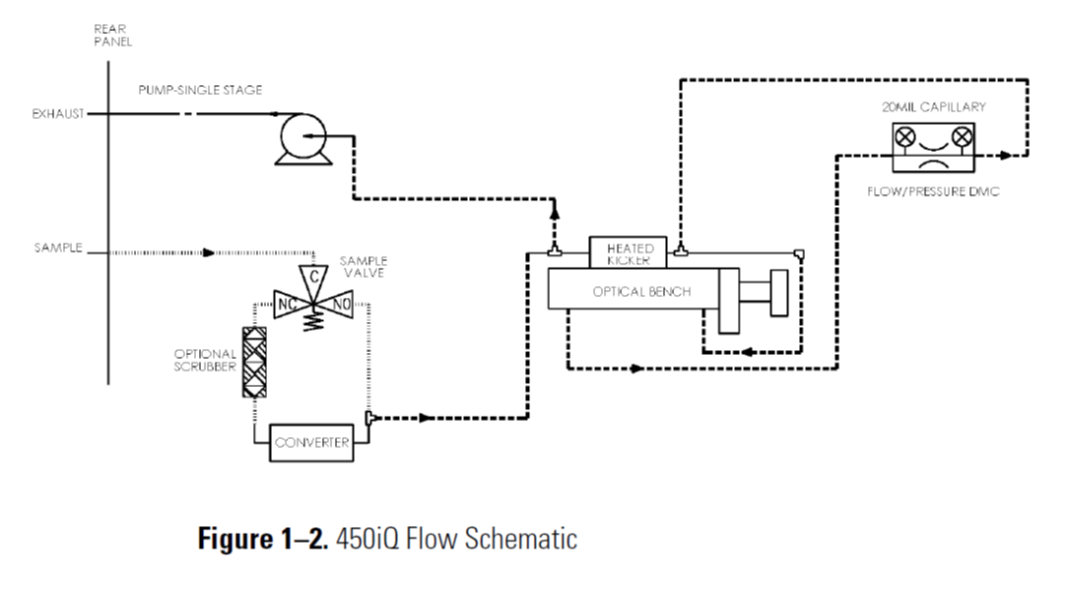
Looking at the Flow Schematic shown below in Figure 1-2, we see the layout of an H2S Analyzer.
This unit includes an internal Air Sample Pump, which draws Ambient Air into the port labeled as SAMPLE. The next component is a SAMPLE VALVE which will direct the H2S Sample Air through an SO2 Scrubber, shown as Optional Scrubber in the diagram. This Scrubber removes SO2 from the Sample Air, so that there is no SO2 included in the final reading, only H2S will be reported. From there, the H2S Sample Air passes through an H2S to SO2 Converter, that is heated to 325 degrees Celsius, which converts H2S back into SO2.
The converted SO2 Sample Air then enters the OPTICAL BENCH. This Optical Bench chamber has a pulsed Ultra Violet Lamp, which flashes UV light into the Optical Bench. The flashing UV Light excites the converted SO2 molecules of the Sample Air. As the excited SO2 molecules decay to lower energy state, they emit an Ultra Violet light that is proportional to the SO2 concentration.
The UV light from the excited SO2 molecules are then detected by a photomultiplier tube (PMT), which is a sensitive UV light detector.
The converted SO2 molecules are reported on the analyzer front display as H2S.
The H2S number is displayed in either Parts Per Billion PPB or Parts Per Million PPM.
The data from the H2S analyzer can be collected either by Analog Voltage Output or Ethernet Output, to an external datalogger.
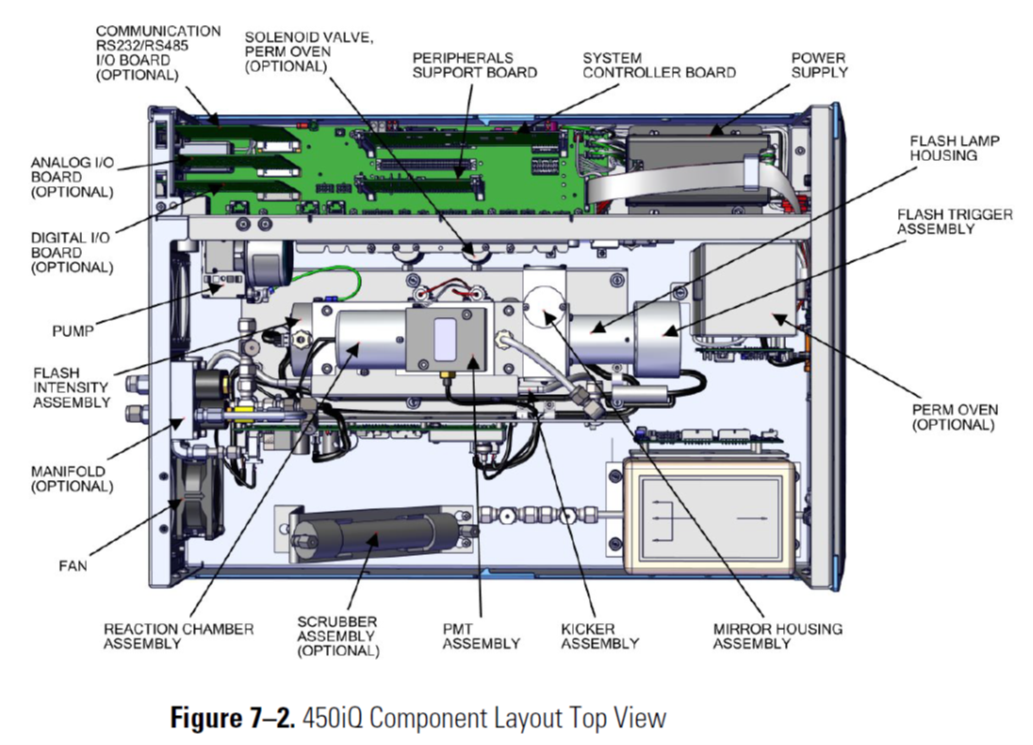
H2S Analyzer Component Layout